Natural Diamond vs. Lab-Grown Diamond
Natural Diamond vs. Lab-Grown Diamond: The Complete Guide for 2025
When buying an engagement ring, wedding band, or fine jewelry, one of the biggest decisions you’ll face is choosing between a natural diamond and a lab-grown diamond. Both are real diamonds, both sparkle brilliantly, and both can symbolize love and commitment. But the differences in origin, value, price, and perception can influence your choice in a big way.

This in-depth article will cover everything you need to know about natural vs lab-grown diamonds: how they’re made, their differences in beauty and durability, their environmental impact, market value, and what’s best for your unique situation.
By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to confidently choose the diamond that best fits your values, budget, and lifestyle.
What Are Natural Diamonds?
Natural diamonds are carbon crystals formed deep in the Earth’s mantle 1–3 billion years ago. They’re created under intense heat and pressure, then brought closer to the surface through volcanic eruptions. Over time, they are mined, cut, and polished into the gems we see in jewelry stores.
Key facts about natural diamonds:
-
Composed of pure carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice.
-
Formed naturally in the Earth’s crust over billions of years.
-
Mined across the world in countries like Botswana, Russia, Canada, and South Africa.
-
Each diamond is unique, shaped by Earth’s natural processes.
Because of their rarity and history, natural diamonds carry a strong cultural and symbolic value. They’re often seen as heirlooms and are still the traditional choice for engagement rings.
What Are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
Lab-grown diamonds (also known as man-made diamonds or synthetic diamonds) are created in laboratories using advanced technology that mimics the conditions under which natural diamonds form. These processes take weeks or months, not billions of years.
Two main methods are used:
-
HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature): Simulates the high heat and pressure conditions deep underground to grow a diamond crystal.
-
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Uses carbon-rich gas to build up diamond layers atom by atom.
Key facts about lab-grown diamonds:
-
Chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds.
-
Often 60–80% cheaper than natural diamonds of similar quality.
-
Certified by the same grading labs (GIA, IGI) that grade natural diamonds.
-
Increasingly popular due to affordability and sustainability concerns.
Unlike diamond simulants (such as cubic zirconia or moissanite), lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds with the same hardness (10 on the Mohs scale), brilliance, and durability as natural stones.
Natural vs. Lab-Grown Diamonds: The Major Differences
1. Origin & Formation
-
Natural: Formed naturally in Earth’s mantle over billions of years.
-
Lab-Grown: Created in weeks in a laboratory environment.
2. Appearance
-
To the naked eye: Indistinguishable.
-
To experts with instruments: Growth patterns and inclusions may differ under advanced testing.
3. Price
-
Natural: Pricier due to rarity and traditional demand.
-
Lab-Grown: 60–85% less expensive, allowing buyers to get a larger or higher-quality stone within budget.
4. Value & Resale
-
Natural: Historically retains more value and may appreciate.
-
Lab-Grown: Resale value is significantly lower and continues to decrease as technology advances and supply increases.
5. Ethics & Sustainability
-
Natural: Mining impacts vary by region; modern operations may contribute to community development but also raise environmental concerns.
-
Lab-Grown: Avoids mining but energy use varies—renewable-powered labs have a smaller footprint, while fossil-fuel-powered labs may not.
The 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds are graded on the 4Cs.
-
Cut: Most important factor for sparkle. Always prioritize an Excellent or Ideal cut.
-
Color: Ranges from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow). Lab-grown diamonds often achieve higher color grades at lower prices.
-
Clarity: Refers to internal flaws (inclusions) or surface blemishes. Many lab-grown diamonds are nearly flawless.
-
Carat: Weight of the diamond. Lab-grown allows buyers to afford larger carat sizes at lower costs.
Certification: Why It Matters
Always buy diamonds—natural or lab-grown—with certification from reputable labs like:
A diamond certificate ensures you’re getting exactly what’s advertised and helps with future resale or insurance.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Natural Diamonds
-
Pros: Provides jobs and economic support in diamond-producing countries.
-
Cons: Mining impacts ecosystems, can displace communities, and consumes significant energy and water.
Lab-Grown Diamonds
-
Pros: No mining required, reduced land disruption, more transparent supply chain.
-
Cons: Energy-intensive processes; eco-benefits depend on whether renewable or fossil fuels are used.
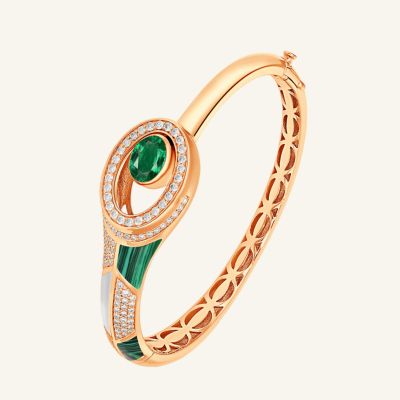
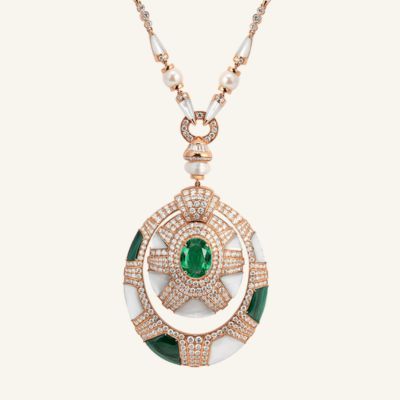
Popular Uses for Natural vs. Lab-Grown Diamonds
-
Engagement Rings: Natural diamonds remain the traditional choice, but lab-grown are increasingly common for affordable, ethical rings.
-
Fashion Jewelry: Lab-grown diamonds allow designers to create bold, large-carat pieces at accessible prices.
-
Heirlooms: Natural diamonds are often chosen for their long-term legacy value.
Browse our Soit Belle Jewels collection today to buy your elegant pieces of jewelry.